42 low gi food labels
› low-gi-explainedLow GI Explained | GI Foundation Understanding the GI value of a food can help you make healthier food choices and improve your overall health in the long run. The GI value of foods is calculated in a food laboratory using valid scientific methods. There are three classifications for GI: Individual food portion: Low: 55 or less Mid: 56 – 69 High: 70+ › resource › glycaemic-indexGlycaemic Index Food Fact Sheet | British Dietetic ... There is good scientific evidence to suggest that basing your diet on low GI foods and keeping an eye on the total amount of carbs you eat, may help to control blood glucose levels for people with type 2 diabetes. Choosing low GI foods as part of a balanced diet can help to minimise fluctuations in blood glucose levels.
› food-labellingFood Labelling | FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization of ... Geographical Indication (GI) labels, boasting an annual trade value of over$50 billion worldwide, are legal tools that link food products to their place of origin, providing both economic, social and environmental value to rural regions. These labels are given to products with specific attributes, qualities or reputation stemming from their ...
Low gi food labels
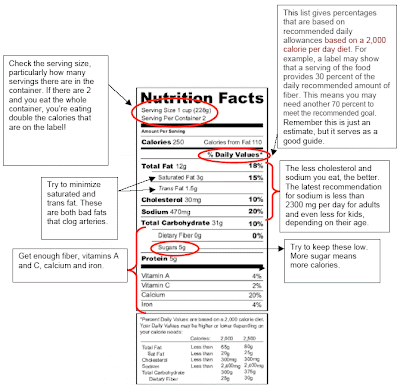
› how-to-read-food-labelsHow to read food labels | healthdirect The label may make a number of nutrition claims such as 'gluten free', 'low GI', 'low fat', 'reduced salt' or 'high fibre'. These mean the product meets strict criteria set by the government. But just because a product can make a nutrition claim doesn't mean it is healthy. › article › 470019-sourdoughSourdough Bread & Blood Sugar | livestrong Just because sourdough bread is a low GI food does not mean you should eat it in excess. One regular slice of sourdough bread counts as one grain serving. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, healthy adults should eat between five and eight servings of grains each day -- half of which should be whole grains. med.virginia.edu › ginutrition › wp-contentLow Sodium Diet - University of Virginia School of Medicine Reading Nutrition Labels You should get in the habit of checking food labels for the most up-to-date information. Sodium is always on the food label. These steps will help you figure out how much sodium is in a certain food: 1. Number of servings and mg of sodium – The label gives you the serving size and the number of servings in the package.
Low gi food labels. › food › nutritionWhat Is Glycemic Index? - Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Nov 19, 2019 · Glycemic load, or GL, is a formula that corrects for potentially misleading GI by combining portion size and GI into one number. The carbohydrate content of the actual serving is multiplied by the food's GI, then that number is divided by 100. So for a cup of beets, the GL would be: 13 times 64 = 832 divided by 100 = a GL of 8.3. med.virginia.edu › ginutrition › wp-contentLow Sodium Diet - University of Virginia School of Medicine Reading Nutrition Labels You should get in the habit of checking food labels for the most up-to-date information. Sodium is always on the food label. These steps will help you figure out how much sodium is in a certain food: 1. Number of servings and mg of sodium – The label gives you the serving size and the number of servings in the package. › article › 470019-sourdoughSourdough Bread & Blood Sugar | livestrong Just because sourdough bread is a low GI food does not mean you should eat it in excess. One regular slice of sourdough bread counts as one grain serving. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, healthy adults should eat between five and eight servings of grains each day -- half of which should be whole grains. › how-to-read-food-labelsHow to read food labels | healthdirect The label may make a number of nutrition claims such as 'gluten free', 'low GI', 'low fat', 'reduced salt' or 'high fibre'. These mean the product meets strict criteria set by the government. But just because a product can make a nutrition claim doesn't mean it is healthy.

-PDF.png?resize=618%2C402)










Post a Comment for "42 low gi food labels"